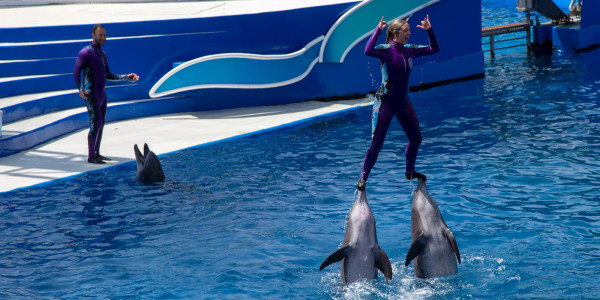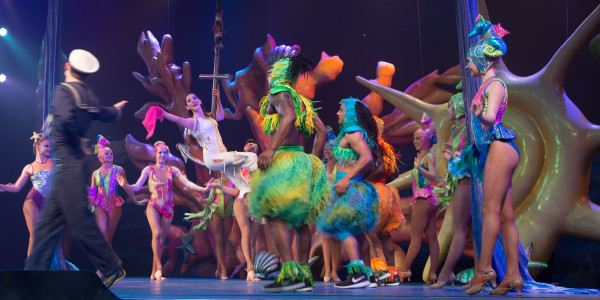Osaka Local Favorites and Must-Do Experiences Japan
Osaka is Japan's vibrant third-largest city and undisputed food capital, offering an intoxicating blend of ancient traditions and cutting-edge modernity. It captivates every traveler with experiences ranging from historic castles and tranquil temples to dazzling neon-lit districts and world-class culinary delights. The city's unique, relaxed yet energetic character, along with its famous "Kuidaore" (eat until you drop) philosophy, makes it an unforgettable destination that will redefine your perception of Japan.
Perfect Blend of Sacred Deer, Buddhist Art, and Culinary Heritage Nara Japan
Nara, Japan's former capital, offers a captivating journey back in time, just a short distance from Osaka and Kyoto. Despite ongoing renovations to some famous landmarks like Kōfuku-ji Temple, the city provides an enchanting experience with its preserved ancient Buddhist culture, including iconic sites like the Nara National Museum and the awe-inspiring Tōdai-ji Temple, home to the Great Buddha. What truly sets Nara apart is the harmonious coexistence of sacred, free-roaming sika deer in Nara Park and its enduring culinary traditions, such as kakinoha-zushi, creating a unique blend of history, nature, and spirituality that captivates visitors.
Osaka World Expo 2025 Cultural Performances That Stole My Heart in Japan
The Osaka World Expo 2025, running from April 13 to October 13, 2025, on Yumeshima Island, is a spectacular celebration of human achievement and cultural diversity under the theme "Designing Future Society for Our Lives." Its centerpiece is the Grand Ring, the world's largest wooden structure, designed by Sou Fujimoto, which serves as both a magnificent architectural marvel and a functional elevated walkway providing shelter and breathtaking night views. The Expo offers an unparalleled culinary journey with diverse food stalls from across the globe, particularly highlighting the rich flavors and cultural stories of the Southeast Asian pavilions like Vietnam, the Philippines, and Malaysia.
Kyoto Part 3: Scenic Dining Trains Traveling to Amanohashidate and Ine Kyoto Japan
This enchanting journey through Kyoto Prefecture begins with a breathtaking cable car ascent to Amanohashidate Viewland, where visitors can witness the legendary sandbar transform into a "Flying Dragon View" by peering through their legs. The adventure continues aboard the luxurious Tango Otohime Gozen dining train, offering a culinary exploration of local delicacies inspired by the Urashima Taro folktale, complete with scenic stops and a special temple seal. The day culminates in the timeless fishing village of Ine, where a boat tour among friendly seagulls provides unparalleled views of traditional funaya (boathouses), followed by tranquil moments at a waterfront coffee shop and a delicious seafood dinner overlooking the bay.
Kyoto Part 2: Cultural Immersion and Modern Discoveries Kyoto Japan
Kyoto is offering a dynamic blend of traditional arts, crafts, and modern entertainment. Visitors can immerse themselves in the refined world of geiko and maiko performances in traditional tea houses, witnessing centuries-old dance and music. The city also offers unexpected delights like the Yamazaki Whisky Distillery Museum, showcasing Japan's mastery in adapting foreign techniques with a local touch. For those seeking contemporary experiences, the Nintendo Center highlights the gaming giant's Kyoto origins and its fusion of traditional Japanese design with modern entertainment.
Kyoto Part 1: Discovering Kyoto Hidden Spiritual Heart Kyoto Japan
Kyoto is more than just a famous travel destination; it's a living museum filled with hidden spiritual traditions that offer a deeper connection to Japan's ancient soul, beyond its well-known temples and bamboo groves. I discovered the true essence of the city through experiences like the Chinowa Kuguri rituals for purification, passing through the Stone of Transformation at Yasui Kompiragū Shrine to sever negative ties and invite good fortune, participating in communal sacred circle ceremonies at Azumamaro Shrine, and meditating while walking through the thousands of vermillion gates of Senbon Torii.
Discovering Hiroshima Spiritual Transformation and Island Treasures Japan
Stepping off the shinkansen into Hiroshima is an emotionally profound experience, a journey through history, healing, and the remarkable resilience of the human spirit. The city, once the tragic ground zero, has transformed into a beacon of peace activism and cultural preservation. Key sites like the Hiroshima Peace Memorial Park with its poignant monuments and the skeletal remains of the A-Bomb Dome serve as powerful, enduring testaments to the past. The city masterfully balances the weight of history with moments of spiritual serenity and the warmth of local culture, creating a uniquely moving and hopeful experience.
Everland Theme Park Spectacular Fireworks Experience South Korea
Everland, South Korea's premier theme park, offers a captivating blend of thrilling rides, diverse themed zones, and stunning seasonal gardens. From the panoramic views afforded by the Sky Cruise cable car and heart-pounding attractions like the T-Express and Thunder Falls, to the ever-changing beauty of the Four Seasons Garden and the spectacular Moomin-themed multimedia fireworks show, Everland provides a uniquely immersive and memorable experience for visitors of all ages, seamlessly blending Korean hospitality with world-class entertainment.
Discovering Seoul Ultimate Street Food Heaven in Myeongdong South Korea
Myeongdong Market in Seoul is a vibrant culinary hub, boasting over 200 vendors that transform evening strolls into extraordinary gastronomic adventures. It offers a wide array of sweet and savory street foods, from unique ice creams like marshmallow and fish-shaped bungeoppang to traditional favorites like spicy fish cakes and dumplings. Visitors can also enjoy innovative takes on classic dishes, such as Korean corn dogs with stretchy mozzarella and diverse fried chicken preparations, alongside refreshing fruit cups and a variety of substantial options like kimchi roll pork belly and baked whole potatoes. It's wise to bring cash as it's still preferred by many vendors.
When Shopping Malls Meet Safari Dreams at Zoolung Zoo South Korea
An extraordinary urban adventure awaits visitors to Seoul's Times Square Mall, where Zoolung Zoolung, Korea's first indoor animal theme park, offers a unique opportunity to interact closely with diverse creatures like toucans, sloths, and bunnies on the 5th floor. This innovative attraction seamlessly blends a vibrant shopping experience with an intimate natural wonderland, allowing for fence-free encounters and educational engagement, culminating in the surprising possibility of witnessing an impromptu K-pop performance in the mall lobby, showcasing Seoul's dynamic fusion of nature, culture, and urban life.
Soaring Above Seoul: A Magical Journey to N Seoul Tower South Korea
The Namsan cable car offers a romantic ascent to N Seoul Tower, where visitors are treated to panoramic views of the city transforming into an urban tapestry. At the summit, thousands of colorful love locks symbolize countless stories of devotion, creating a unique visual and auditory experience. Inside the tower, the observation deck provides a breathtaking 360-degree vista of Seoul's blend of ancient and modern, with the Han River weaving through the expansive cityscape. The complex also features dining and gift shops, making the entire experience a memorable blend of adventure, romance, and urban exploration.
The Royal Guard Changing Ceremony at Gyeongbokgung Palace South Korea
The Royal Guard Changing Ceremony at Gyeongbokgung Palace's Gwanghwamun Gate in Seoul, is a historically authentic reenactment of Joseon Dynasty royal security protocols, featuring elaborately dressed guards with traditional weapons and instruments. This captivating 20-minute spectacle, which began in 2002, offers a vibrant glimpse into Korea's royal heritage and serves as an excellent starting point for exploring the palace grounds and the nearby Bukchon Hanok Village, where visitors can experience traditional Korean residential architecture and culture.
London Most Stylish Street Party at Chelsea in Bloom Ultimate Floral Extravaganza
Chelsea in Bloom 2025 will celebrate its 20th anniversary from May 19-25 with the theme "Flowers in Fashion," transforming the elegant streets of Chelsea into London's largest free-to-attend floral festival. This year's event will showcase the intersection of haute couture and horticulture, with retailers, restaurants, and hotels competing to create stunning floral interpretations of iconic fashion moments. Visitors can enjoy a unique, immersive experience, vote for their favorite displays, and explore one of London's most prestigious neighborhoods.
Hampton Court Palace Free Garden Day and the Bushy Park Parade
A visit to Hampton Court Palace experienced a unique combination of its annual Free Garden Day and the Bushy Park Parade, transforming a regular weekend into a journey through royal history and community celebration. The palace's 60 acres of meticulously maintained gardens, including the 1768 Great Vine producing 600 pounds of grapes annually and the historically accurate Kitchen Gardens, offered a free feast for the senses with their diverse horticultural wonders and heritage seed program. Seamlessly transitioning to Bushy Park, I enjoyed the parade, a community event amidst the park's 1,100 acres.
Magical Morocco Exploring Marrakesh, Casablanca, and Essaouira
Morocco offers a vibrant tapestry of experiences, from the bustling markets and street food scene of Marrakesh's Jemaa el-Fnaa, where evenings are a sensory overload of sights, sounds, and flavors including local delicacies like snail soup, to the tranquil yet dramatic landscapes of the Agafay Desert for sunset camel rides and magical nights under the stars with traditional feasts and fire shows. The adventure also extends to the natural beauty of the Atlas Mountains, home to the impressive Ouzoud Waterfalls, providing a refreshing contrast to the urban and desert explorations and showcasing Morocco's diverse appeal.
When a moment in front of me appears to be particularly special, whether it be by beauty or experience, I capture it. I usually find a reason to justify taking that photo – symmetry, or color or contrast – and it’s my hope that my photography sheds light onto what I see and do on a daily basis. - Connor Franta
Street Food, Scenic Views, and Ancient Wonders from Naples to Sorrento Italy
Naples and Sorrento in Italy offer a unique blend of art, history, food, and breathtaking landscapes. From street food to ancient ruins like Pompeii, this region has something for every kind of traveler. Explore Naples' culinary delights, scenic views on the Amalfi Coast, iconic towns, and luxury villas, as well as visit Capri's famous Blue Grotto and experience the magic of this Italian destination.
Discovering Amsterdam’s Charm and Lights in Winter
Winter in Amsterdam offers a unique charm with twinkling lights on canals, cozy cafes, and fewer crowds. Explore historic houses, festive markets, and iconic attractions like the Amsterdam Light Festival and Eye Filmmuseum, which transforms into a dazzling outdoor gallery during winter. Enjoy Dutch pancakes, stroopwafels, and burgers, and discover traditional activities like wooden shoe-making and visiting Zaanse Schans windmill village.
A Swiss Christmas Dream Exploring Zurich Switzerland
Zurich transforms into a winter wonderland during Christmas, with twinkling lights, festive markets, and breathtaking Alpine views. Explore the city's Christmas markets, including the Christkindlimarkt at Zurich Main Station and Wienachtsdorf at Sechseläutenplatz, and visit iconic landmarks like Lindt Home of Chocolate and Grossmünster. Take a snowy day trip to Grindelwald and Interlaken for a fairytale-like escape, and stroll through the charming Old Town's cobbled streets lined with festive decorations and historic buildings.
Uncovering Portugal's Layers from Porto Hills to the Douro Valley in Portugal
This Portuguese adventure journeyed from the vibrant, historic city of Porto, celebrated for its stunning panorama, architectural marvels like the Dom Luís I Bridge, and lively Ribeira district, south to the sun-kissed Algarve, with significant exploration in between. A deep dive into the world of Port wine in Vila Nova de Gaia and the breathtaking, terraced landscapes of the Douro Valley, with its quintas and river cruises, offered a taste of the region's renowned liquid gold and surreal scenery.
London Christmas Photography Portfolio Builder Day
The London Christmas Photography Portfolio Builder Day offered a festive backdrop with twinkling lights, holly wreaths, and vintage-style decorations for photographers to capture magazine-worthy images. Two professional models showcased elegant holiday ensembles, sharing tips on posing and encouraging collaboration among participants. The event provided diverse scenes and prop opportunities, culminating in a memorable experience for photographers.
City of London Photowalk with Model Tyana and Ariana
A blog post about a photowalk in London features two professional models, Tyana and Ariana, who joined a group of photographers for a 3-hour shoot. The photowalk showcased the contrast between old and new London, capturing stylish autumn fashion looks against historic landmarks and modern architecture, resulting in striking and timeless images.
A Day with Mila Ballet Model in London
The blog post describes a photo shoot with ballet model Mila in London, where she showcases her exceptional technique and artistic expression. The photographer praises Mila's calm demeanor, professionalism, and collaborative spirit, highlighting the effortless beauty of their work together, from soft natural light to captivating choreographed moments.
Fusion of Fun and Fine Art at Foundation LV Paris
The Jardin d'Acclimatation is a blend of natural beauty, entertainment, and cultural history in Paris, featuring a modern masterpiece, the Louis Vuitton Foundation. The garden, originally established in 1860, offers rides, attractions, art installations, and animal enclosures, making it a delightful time capsule with something for everyone.
A Glimpse into the Monet's Life in Giverny France
Giverny, France is a treasure trove for art lovers and nature enthusiasts, where Claude Monet spent the last 43 years of his life. The iconic Claude Monet House offers a glimpse into Monet's personal world, while the gardens are an explosion of color and tranquility, showcasing Monet's skill as a painter and horticulturist.
Exploring Montmartre Through John Wick Fight Staircase
The blog explores the artistic and cinematic gems of Montmartre, a charming neighborhood in Paris. The staircase featured in "John Wick: Chapter 4" is highlighted, followed by visits to the stunning Basilique du Sacré-Cœur and vibrant Place du Tertre, where artists showcase their work amidst a lively atmosphere.
Beaches of Bravery at Normandy D-Day Landings France
This blog takes readers on a journey through five beaches where Allied forces landed during the D-Day invasion, including Utah Beach in Normandy, France. The blog visits each beach, exploring its history and significance, as well as stopping at museums, memorials, and landmarks such as Le Roosevelt Café and Pointe du Hoc.
The Architectural and Artistic Wonders of Musée d'Orsay Paris
The Musée d'Orsay museum was originally built as the Gare d'Orsay railway station in 1900. It narrowly escaped demolition due to its architectural beauty and historical significance, and was converted into a museum by 1986. The building boasts an extensive collection of art from the 19th and early 20th centuries, including works by Monet, Van Gogh, and Renoir, with notable highlights in a gallery dedicated to Van Gogh and a striking clock still ticking today.
Emperor's Eternal Home at Tomb of Napolean Paris
The tomb of Napoleon Bonaparte is located under the Hôtel des Invalides in Paris, built between 1842-1861. It's designed to reflect his status as a military genius and leader, with a grand crypt and ornate decorations celebrating his achievements. The sarcophagus, made of red quartzite, weighs 18 tons and is surrounded by intricate details, creating a sense of reverence and awe for the historical figure.
Duels The Art of Fighting at Army Museum Paris
The Army Museum Paris features an extensive collection of military artifacts, including medieval armor, modern uniforms, and artillery shells. Its latest exhibition, "Duels - The Art of Fighting," explores the history and culture of dueling from its origins to its decline in the 19th century, offering a comprehensive look at this fascinating and often perilous practice.
Secret Entrances to the Louvre Paris
To avoid long lines at the main entrance, consider visiting the Carrousel du Louvre, an underground entrance with short wait times (usually 5 minutes) that grants access to the same areas as Le Pyramide. After passing security, spend more time exploring the museum's vast collection of artworks and history.
Churches, Palaces, and History: Discovering Paris on Foot
This 7-stop walking tour explores Paris' historical and cultural landmarks, including Église Saint-Germain l'Auxerrois, Louvre Palace, Comédie-Française, Bibliothèque Nationale de France, Place Vendôme, Sainte-Chapelle, and Notre-Dame Cathedral.
Inside the Magnificent Versailles Palace France
The Palace of Versailles was built by King Louis XIII in 1623 as a hunting lodge but transformed by his son, King Louis XIV, into an extravagant palace reflecting absolute monarchy. The palace features classical French Baroque style, including the Hall of Mirrors with its original practical use to reflect sunlight and candlelight.
The Artistry of the Gardens of Versailles France
The Gardens of Versailles were designed by André Le Nôtre for King Louis XIV in the late 17th century as part of his Palace of Versailles vision. The gardens feature meticulously manicured lawns, geometric flower beds, grand fountains, and sculptures over 800 hectares in size, reflecting classical French garden style with symmetry and order.
Sparkling Lights on Eiffel Tower Paris
The Eiffel Tower was built in 1887-1889 for the World's Fair and initially met with criticism. Standing at 324 meters tall, it became a beloved symbol of Paris and a marvel of engineering. The tower now attracts millions of visitors with its breathtaking views and rich history, featuring three accessible levels, shops, and a stunning light show every hour on the hour from dusk to 1 AM.
London on Foot: From Museums to Monarchy
This walking tour explores iconic landmarks in London, including the Natural History Museum, Victoria and Albert Museum, Science Museum, Albert Memorial, London Bridge, Palace of Westminster, Buckingham Palace, and Piccadilly Circus. The tour combines history, culture, art, science, and entertainment, offering a diverse experience for visitors.
Yeoman Warders and Hidden Treasures at Tower of London UK
The Tower of London has a 1,000-year history as a royal palace, prison, armory, and zoo. It's where notorious prisoners like Anne Boleyn and Lady Jane Grey met their end in gruesome executions. The Tower also boasts a ravens population that's kept at all times to prevent the kingdom's downfall according to legend. Visitors can explore the White Tower, Crown Jewels display, and learn from Yeoman Warders about its dark history and captivating stories.
London Photo Challenge at Tate Modern
The author participated in a photo challenge at Tate Modern Museum in London, capturing reactions and expressions of visitors as they engaged with modern art. The challenge aimed to document human emotions evoked by diverse exhibits, from awe and joy to confusion and puzzlement. The resulting photographs told vivid stories of the human experience, showcasing the power of creativity and connections through art.
Discovering the Spiritual Heart at Westminster Abbey London
Westminster Abbey is a historic site with origins dating back to the 960s, featuring a Gothic architectural style. The abbey has played a central role in British history, hosting coronations, royal weddings, funerals, and significant state events. It is also home to notable figures' graves, including monarchs, poets, scientists, and politicians, as well as artifacts like the oldest door in Britain and the Coronation Chair, which has been used since 1308.
From Waiters Races to Waggiest Tails: Fun at the Soho Fete
The Soho Village Fete is a vibrant celebration that combines traditional village fete traditions with the area's quirky charm and bohemian spirit. Held in July 2024, the event features eclectic performances, games, and competitions, including a magic show, tug of war, spaghetti eating contest, waiter's race, dog show, and live music. It's a day that honors Soho's past while embracing its new and exciting aspects, making it a must-visit for locals and visitors alike.
Unveiling Ancient Mysteries of Stonehenge UK
Stonehenge is a prehistoric stone circle in Wiltshire, England, built around 2500 BC. It's a site of debate and speculation about its purpose, with theories ranging from ceremonial to astronomical observations. Visitors can explore the monument, exhibitions, and learn about its construction, which involved transporting massive stones over 150 miles from Wales using unknown methods.
Exploring Windsor Castle's Majestic History UK
Windsor Castle was founded in the 11th century by William the Conqueror as a motte-and-bailey castle to protect Norman dominance around London. Over centuries, it was expanded and transformed into a luxurious royal palace under King Henry III and elevated by King Edward III, who established the Order of the Garter. Today, visitors can explore opulent State Apartments, St. George's Chapel, and witness the Changing of the Guard.
The Healing Waters of Roman Baths
The Roman Baths in Bath, Somerset, are a testament to Roman engineering and architecture. The natural hot springs supply warm water to the baths, which feature an impressive Great Bath with ancient columns and statues. Visitors can explore the temple courtyard, see artifacts like the gilt bronze head of Sulis Minerva, and discover over 130 curse tablets inscribed with messages from wronged bathers.
London Journey Through Time Trial
The "Journey Through Time" trail in London's Heritage Quarter features 11 sculptures representing iconic British symbols, accompanied by augmented reality content revealing historical insights and archival imagery. The trail runs from June 15th to August 4th and offers a free, family-friendly experience with QR codes, interactive talks, and walking tours.
A Journey Through Poland's Cultural Jewel Kraków Poland
Kraków, a UNESCO World Heritage city in Poland, offers a rich cultural experience with cobblestone streets, medieval architecture, and a vibrant arts scene. Visitors can explore the Rynek Główny market square, St. Mary's Basilica, Wawel Royal Castle, and Vistula River for a glimpse into Poland's history and resilience.
A Medieval Marvel: Discovering the Historic Charm of Lincoln UK
Lincoln UK is an underrated English city offering rich history and modern comforts. The medieval cathedral and castle provide breathtaking views, while the charming shops and eateries cater to all tastes. Visitors can explore historic sites like Lincoln Castle and Jewish House Books, or enjoy panoramic views from a tower tour. With its authentic feel, Lincoln captivates with its unique blend of past and present, making it an unforgettable weekend getaway or extended holiday destination.
Las Vegas Street Life and Iconic Sights
Las Vegas is a photographer's dream destination, offering endless visual opportunities from its vibrant street performers to iconic landmarks like The Venetian Resort and the Eiffel Tower. From gondola rides in The Venetian's Grand Canal to the light show at the Eiffel Tower, photographers can capture stunning images of the city's Italian charm, grand architecture, and eclectic nightlife.
Photographic Tour of Downtown San Jose
San Jose offers a mix of modern architecture, historic landmarks, and vibrant public art for photographers to capture. Visit the San Jose Museum of Art, Center for the Performing Arts, Adobe Headquarters, and tech museums like the Tech Museum of Innovation to take in its unique sights, from sleek designs to whimsical installations, and explore its rich history and cultural narratives through sculptures, memorials, and historic theaters.
Charming Coastal Town Sitges Spain
Sitges, Spain is a charming coastal town located near Barcelona, boasting 17 pristine beaches, cobalt blue doorways, and whitewashed Mediterranean buildings. The town features the stunning Església de Sant Bartomeu i Santa Tecla church with breathtaking views of the Mediterranean Sea, as well as Museu del Cau Ferrat showcasing Catalan Modernisme art.
Barcelona's Best: Sagrada Familia, Flamenco, and Foodie Finds
Mercado de La Boqueria is a must-visit for any foodie, this market is a feast for the eyes as well as the taste buds. The stalls overflow with fresh, seasonal ingredients, including locally sourced vegetables, glistening fish, and an array of meats. Don't miss the artisanal cheeses, cured hams, and sausages on display. From the vibrant markets to the creative restaurants, Barcelona offers an incredible culinary experience that will leave you wanting more. Bon appétit!
You can look at a picture for a week and never think of it again. You can also look at a picture for a second and think of it all your life. - Joan Miro
Nighttime Majesty of Shanghai China
The article features Shanghai China as its main destination. It highlights Peking duck as a centuries-old Chinese dish, and also mentions a visit to the Top of Shanghai Observatory for panoramic views of the city. Additionally, it describes Nanjing Walking Street as one of the world's famous shopping destinations with global brands, local boutiques, street performers, and modern amenities like Apple Stores.
Temples and Scenic Wonders in Enoshima and Kamakura Japan Day 11
Take a day trip to Enoshima and Kamakura, about an hour from Tokyo. Explore ancient temples like Kotoku-in and Hasedera Temple, and vibrant streets like Komachi-dori Street in Kamakura. Ride the scenic Enoden Line train and visit Enoshima Shrine, with its blessings for love, finances, and business. Enjoy local cuisine, stunning views, and a taste of Japanese culture before returning to Tokyo.
Art Aquarium Ginza Japan Day 10
The Art Aquarium Museum in Tokyo features over 30,000 goldfish swimming through tanks of various shapes and sizes. The exhibit is a multi-sensory experience with artworks as tanks and zones that transport visitors to different realms, including a procession of courtesans and the ethereal Forest of Goldfish.
Hakone Ropeways, Pirate Ships, and the Allure of Fuji Japan Day 9
The blog post is about Hakone, Japan, a charming destination known for its hot springs, natural beauty, and unique experiences. The author shares their adventures, including visiting Mount Fuji, soaking in onsen culture, sailing pirate ships on Lake Ashi, and trying local cuisine like sushi, soba noodles, and ice cream with unique flavors.
Harry Potter Studio Tour Japan Day 8
The Harry Potter Studio Tour Tokyo is an immersive experience where fans and newcomers can explore the magical world of Harry Potter. Visit iconic locations like Platform 9¾, Hogwarts Castle, Ollivanders, and Diagon Alley, and participate in activities like wand-choosing, Quidditch matches, and butterbeer tastings.
Odaiba Unleashed with Miniature Marvels and Arcade Adventures Japan Day 7
Odaiba, Tokyo's entertainment hub, offers a unique experience with its miniature park and arcade games. The "Small World" features scaled-down landmarks, while Joypolis is an indoor amusement park with traditional arcade games, interactive attractions, and cutting-edge VR experiences. Visitors can enjoy roller coasters, games, and immersive virtual reality adventures amidst a lively atmosphere that ignites the inner child and leaves visitors in awe of imagination.
Sensō-ji Temple A Gateway to Tokyo's Rich Cultural Heritage Japan Day 6
SENSŌ-JI Temple, located in Tokyo's Asakusa district, is a 1,000-year-old sanctuary offering spirituality and culture. The temple features a magnificent Kannon statue, five-story pagoda, and Zen gardens, as well as the Thunder Gate, which welcomes visitors with two colossal statues of Wind and Thunder gods. A purification ritual at the Chozuya fountain and Omikuji divination stalls are also available.
National Museum of Nature and Science Japan Day 5
The National Museum of Nature and Science in Japan is a treasure trove of knowledge showcasing fossils, astronomy, and scientific wonders. The museum invites visitors to explore the past, present, and future through exhibits on paleontology, biodiversity, and innovation, offering interactive displays and hands-on experiences for all ages, leaving a renewed sense of wonder and awe upon departure.
Yokohama Custom Cup Noodles to Life-Sized Gundam Magic Japan Day 4
The Cup Noodle Museum, Ramen Museum, and Gundam Factory in Yokohama offer interactive exhibits, immersive experiences, and hands-on activities for noodle lovers, anime fans, and history enthusiasts. The museums feature colorful displays, nostalgic atmospheres, and opportunities to design cup noodles, make ramen, and interact with life-sized Gundam sculptures.
Tokyo Opera City Art Gallery Japan Day 3
The Tokyo Opera City Art Gallery offers a visual feast and a journey through art history, with a collection of artistic expressions spanning eras and styles. The gallery showcases traditional Japanese painting, Western impressionism, and contemporary works that challenge conventions and spark conversations. Its architecture is a harmonious composition of light and space that complements the artworks, creating a unique experience for visitors.
Lake Kawaguchiko From Ninja Legends to Mount Fuji Magic Japan Day 2
The blog describes a journey around Lake Kawaguchiko in Japan, exploring its history, culture, and natural beauty. The itinerary includes activities such as ninja training, scenic boat rides, and panoramic views of Mount Fuji, as well as visits to historical sites like the Ninja Village and ramen restaurants offering breathtaking views.
Shinjuku Skyscrapers, Squishies, and the Roar of Godzilla Japan Day 1
This blog post highlights the top spots to visit in Shinjuku, Tokyo's bustling district. The Tokyo Metropolitan Government Building Observation Deck offers panoramic views of the city and Mount Fuji. The Love Sign and Godzilla Statue are iconic attractions that capture the essence of love and pop culture. Other unique experiences include a gaming arcade center, cat cafe, sensory wonderland (Mooosh Squishy), Rainbow Cotton Candy, and Pokémon Center, making Shinjuku a vibrant fusion of modernity and tradition.
The American Harp Society Performance
The 25th National Competition of the American Harp Society took place at the Colburn School in Los Angeles from May 31 to June 4, 2023. The event was open to harpists aged 30 or under who are US citizens or members of the Americas, and featured a pre-concert program by the San Jose Youth Symphony Harp Ensemble.
Vacation in LA: Iconic Sights, Hidden Gems, and Culinary Adventures
The blog features a traveler's journey through Los Angeles, covering various attractions such as the La Brea Tar Pits, Los Angeles County Museum of Art, and NASA's Space Shuttle Endeavour. The writer also visits iconic landmarks like Venice Beach, Santa Monica Pier, and shares recommendations for restaurants with unique flavors, including White Elephant, Du-Pars, Urth Caffe Santa Monica, DTLA Ramen, Holey Grail Donuts, Egg Tuck, and Chuncheon Dakgalbi Donghae Makguksu.
Los Gatos Christmas Holidays Parade
The Annual Los Gatos Children's Christmas/Holidays Parade features Girl Scouts, Boy Scouts, marching bands, drill teams, and floats along the Avenue. The event is sponsored by the Los Gatos Lions Club & LGS Recreation and honors two Grand Marshals: Henry Reyes, a legendary Girls Field Hockey Coach, and George Shannon, a long-time community volunteer.
Guinness Storehouse Dublin Ireland
The Guinness Storehouse in Dublin offers a unique and informative experience, taking visitors through the history of Ireland's iconic beer from its origins 250 years ago to pouring a perfect pint. The self-guided tour is engaging and includes a complimentary drink at the Gravity Bar with stunning views over Dublin. It was highly praised by one visitor as a highlight of their trip to Dublin.
MATC Convention 2022 Los Angeles
The Music Teachers' Association of California (MTAC) Convention in Los Angeles features world-class artists and music educators celebrating music performance and composition. The convention offers opportunities to engage with students, parents, and teachers through various programs such as Certificate of Merit, Piano Concerto Solo Competition, and Young Composers Guild, serving over 4,700 MTAC members statewide.
A Memorable Boat Trip Adventure on Shasta Lake in California
We rented a boat at Silverthorn Resort for a houseboat vacation on Shasta Lake. The lake offers calm waters ideal for swimming, fishing, and water sports. Houseboats have floating "suites" with amenities like swim platforms, slides, BBQs, and modern kitchens. The resort also offers other watercraft rentals, making it an excellent spot for outdoor activities and scenic views.
Boardwalk Beats and Thrills: A Promotion Party at the Santa Cruz Beach Boardwalk June 2022
The Santa Cruz Beach Boardwalk offers a variety of rides, including classic wooden roller coasters like the Giant Dipper, as well as more adventurous options like the Fireball and Double Shot. The boardwalk also features game booths with arcade games, carnival games, and outdoor activities like Sky Glider and Sea Swings, providing something for all ages and thrill levels.
A Celestial Vantage Point: Exploring Griffith Observatory in Los Angeles
The Griffith Observatory in Los Angeles is a popular landmark featuring exhibits, planetarium shows, and stunning views. Located on Mount Hollywood, it has been a California icon since 1935 and has appeared in numerous movies. Admission to the observatory building is free, while parking can be limited on weekends. The complex includes various points of interest, including an Egyptian sundial, James Dean's memorial, and solar telescopes.
Harker Spirit of The Row Dance Show December 2021
Upper school performing arts groups Downbeat, Harker Dance Company (HDC), and Kinetic Krew performed at the Santana Row Tree Lighting ceremony on December 7, 2021. They entertained a large live audience with dance and song, featuring routines to popular holiday songs and festive medleys. The event allowed students to perform without masks, bringing joy and excitement to those who watched.
San Jose Youth Symphony Harp Ensemble November 2021
The San Jose Youth Symphony Harp Ensemble is a music program for students to develop ensemble skills. They perform three concerts per season, including two free community outreach concerts, starting with the Season of Hope Concert in December and ending with their final concert at West Valley College.
Harker Day School Event October 2021
Harker Day combined Family & Alumni Picnic and Homecoming into a full day event on Oct. 9, 2021. The campus saw games, food, sports, and performances, including a tug-of-war contest between freshmen and sophomores won by the Class of 2024. Mini Cat Town was a popular attraction, while varsity teams competed in water polo and volleyball, with mixed results, before falling to Marina High School in the Homecoming game.
Harker Middle School Campus Opening September 2021
Harker Middle School is relocating from its Blackford Ave. campus to a Union Ave. location starting September 2021. The new campus features smaller classrooms, interior hallway doors, and exterior doors for science classes, as well as spacious areas for students to interact in-person after over a year of remote learning. This transition aims to create a fresh start with a new energy, closer community, and improved atmosphere for teachers and students.
It's weird that photographers spend years or even a whole lifetime, trying to capture moments that added together, don't even amount to a couple of hours." - James Lalropui Keivom
Family Fun at Moon Palace Cancun and Xcaret Park December 2019
We stayed at the Moon Palace Hotel in Cancun, Mexico from December 24-31, 2019. The resort is beautiful, clean, and family-friendly with plenty of activities for kids. Rooms were amazing, staff were friendly and polite, and food was fantastic. We also visited Xcaret Park, which offered many activities and excellent customer service, making it a must-do experience in Cancun.
Discovering the World at EPCOT Theme Park Orlando Florida February 2019
Epcot is a theme park at Walt Disney World Resort in Florida, dedicated to human achievement and innovation. Spanning 305 acres, it's known as a "permanent world's fair" with attractions like Test Track, Soarin', and the World Showcase. It hosted 12.444 million guests in 2018, ranking fourth-most-visited theme park in North America and seventh globally. The park is represented by Spaceship Earth, a geodesic sphere.
Stepping into the Fairy Tale of Disney Magic Kingdom Orlando Florida February 2019
Magic Kingdom is a theme park at Walt Disney World Resort in Florida, opened on October 1, 1971. The park welcomed 20.859 million visitors in 2018, making it the most visited theme park worldwide for 13 consecutive years. A nightly fireworks show, known as Happily Ever After, has been running since 1999 and features pyrotechnics, lasers, and music on barges in World Showcase Lagoon.
An Unforgettable Day at Kennedy Space Center Cape Canaveral February 2019
The Kennedy Space Center Astronaut Training Experience (ATX) simulates space missions, including traveling to Mars. Visitors participate in training exercises, taking on roles such as flight director, spacecraft systems officer, and engineer. The experience includes navigating Martian terrain, conducting a spacewalk, and repairing equipment in microgravity. It is a highly recommended attraction with a guided bus tour offering informative insights into the launch pads and unique photo opportunities.
Don't pack up your camera until you've left the location. - Joe McNally
Splashing Fun and Ocean Wonders at Seaworld San Diego August 2018
SeaWorld San Diego offers various attractions, including shows featuring killer whales, sea lions, and dolphins, as well as rides and aquarium exhibits. The Orca show features 11 whales performing choreographed moves, showcasing their unique eating habits and physical characteristics, such as weighing up to 6 tons and having black backs and white bellies.
Exploring the Expansive Zoo Safari Park in San Diego California
The San Diego Zoo Safari Park is an 1,800 acre zoo in California featuring wild and endangered animals from around the world. It includes free-range enclosures with African animals like antelopes, giraffes, and rhinoceros, as well as a bird show and interactive experiences like feeding lorikeets. The park offers unique exhibits and daily shows, including Shiley's Cheetah Run in the late afternoon.
Exploring the USS Midway Museum in San Diego
The USS Midway Museum in San Diego is a museum ship that showcases the longest-serving US aircraft carrier of the 20th century (1945-1992). Opened as a museum on June 7, 2004, it attracts over 1 million visitors annually and is now the most popular naval warship museum in the US, hosting 700+ events, 50,000 students, and 5,000 children each year with interactive features like audio tours, aircraft climb-aboard experiences, and flight simulators.
Action, Excitement, and Movie Magic at Universal Studio California August 2018
Universal Studios Hollywood is a film studio and theme park in San Fernando Valley, Los Angeles County, California. It offers tours of real sets and is one of the oldest and most famous Hollywood studios still in use. The park has 70% of its land within unincorporated county island Universal City, with the rest in LA city limits. In 2017, it hosted over 9 million guests, ranking 15th globally among North American parks.
Experiencing the Magic at Disneyland Park California August 2018
Disneyland Park, opened July 17, 1955, is the first theme park designed by Walt Disney. It was originally a single attraction but has undergone numerous expansions and renovations since its opening, including additions like New Orleans Square in 1966 and Star Wars: Galaxy's Edge in 2019. The park has also welcomed a neighboring park, Disney California Adventure Park, opened on the original parking lot site in 2001.
Stepping onto The Enchanted Hill: A Visit to Hearst Castle California August 2018
Hearst Castle is a National Historic Landmark located on California's Central Coast. Built between 1919 and 1947 by William Randolph Hearst, it features 127 acres of gardens, terraces, pools, and walkways, as well as a main mansion with Spanish and Italian antiques. A private movie theater, zoo, tennis courts, and swimming pools were also part of the estate's opulent amenities.
Cruising California Coast Along The Iconic 17-Mile Drive California August 2018
The 17-Mile Drive is a scenic road through Pebble Beach and Pacific Grove on the Monterey Peninsula in California. The drive hugs the Pacific coastline, passing famous golf courses, mansions, and attractions like the Lone Cypress and Del Monte Forest. It serves as the main road through the gated community of Pebble Beach, where nonresidents pay a toll to use the road.
...looking at, studying, and absorbing good photography serves the same purpose for a beginning photographer. That is because learning the components of a good image - composition, lighting, gesture - and seeing those elements used differently over and over by different masters, makes it easier for a person to achieve the same end on his or her own over time. And there is simply is no alternative to this, no shortcut. - Frank Van Riper
A Retreat of Design: The Commune by the Great Wall Beijing China July 2017
The text describes a blog about visiting the Great Wall of China. The writer shares their experience staying at a private collection of contemporary architecture near the wall, with access to an untouched portion of the wall via a private path. They recommend visiting with a group and renting an entire house to avoid encountering strangers in smaller accommodations.
All-Inclusive Fun Activities at Club Med Sanya China May 2017
Sanya, China is a tropical city on Hainan Island with upscale hotels and water sports, including snorkeling, surfing, and jet-skiing. The city's beautiful islands and beaches are popular spots for swimming and natural scenery, especially Wuzhizhou Island and its coral reefs. Sanya has two peak seasons: winter (Oct-Feb) for Russian tourists escaping cold weather and summer holidays for families like the author who stayed at Club Med Sanya.
Unexpected Animal Encounters at Samjung The Park in Busan Korea May 2017
Samjung The Park is a small zoo located in Busan's Children's Park that offers a fun and interactive way to spend the day with animals. The park has two main sections with walkways that are clean, large, and wheelchair accessible. Prices vary by age group, but the highlight of the zoo is its unique animal interactions, such as daily feeding schedules and meet-and-greets with different animals, including a popular "animal parade" event.
Exploring The Enchanting Gamcheon Cultural Village in Busan Korea May 2017
Gamcheon Cultural Village in Busan, Korea is known as "Korea's Santorini" due to its artistic and historic charm. Originally a religious community, the village was filled with refugees and followers of the Taegukdo Religion after the Korean war. The unique multi-tiered communal layout allows each house to face outward without obstructing others, reflecting the teaching of Yin and Yang harmony.
Sandy Shores and Historic Heights at Haeundae Beach in Busan Korea May 2017
Haeundae Beach is Busan's most famous beach, known for its white sand and shallow bay perfect for swimming. It becomes crowded during summer months with thousands of people and parasols packed into a mile of sand. The beach hosts various cultural events throughout the year, including the "Polar Bear Club" event in January.
You can find pictures anywhere. It's simply a matter of noticing things and organizing them. You just have to care about what's around you and have a concern with humanity and the human comedy. - Elliott Erwitt
Ocean Up Close at Busena Marine Park in Okinawa Japan
Busena Marine Park is an underwater attraction in Okinawa with no need to dive or snorkel, offering a 360-degree view of marine life through its glass-bottom boat and underwater observatory. A free shuttle service connects the park's facilities, making it accessible for families with small children. Visitors can also enjoy feeding fish while waiting to board the boat for a 20-minute tour.
A Visit to Okinawa Churaumi Aquarium in Japan
The Churaumi Aquarium in Okinawa, Japan is considered one of the best aquariums in the world. It features a massive Kuroshio Tank with giant whale sharks and manta rays, as well as various exhibits showcasing marine life from around the globe, including coral, deep-sea creatures, and interactive pools where visitors can touch starfish and seashells.
Experiencing Okinawa World in Japan
Okinawa World is a theme park showcasing Okinawan culture. The park features a massive natural cave (Gyokusendo Cave), a craft village with workshops, and a snake museum. The cave offers spectacular stalactites and stalagmites, while the kingdom village demonstrates traditional crafts like weaving and pottery. Visitors can also explore the Habu Park, which includes a snake show, souvenir shops, and local cuisine restaurant.
Tranquility and Tropical Luxury at JW Marriott Phuket Thailand
The JW Marriott Phuket resort is a kids-friendly destination in Phuket, Thailand, located on Mai Khoa Beach with a wide white sand beach. The resort offers delicious food options, including a Thai restaurant and deli serving sticky buns. It features multiple pools, a waterfall swim-up bar, and a hut offering massages for $8. A nearby shopping mall provides access to restaurants, local shops, and souvenir stores.
Riding the Sky to Taipei Tea Heaven at Maokong Gondola Taiwan
Maokong is a mountain village in Taiwan with breathtaking views of Taipei City. The Maokong Gondola cable car takes visitors to the top at NT$50 each way, offering panoramic views and high-quality tea selection. The village got its name "Maokong" from the Chinese term for the pitted surface of surrounding mountains, which resembles cat scratches, inspired by the area's geology.
Exploring the Ambitious Overseas Chinese Town East in Shenzhen China
Overseas Chinese Town East in Shenzhen features two theme parks: Knight Valley and Tea Stream Resort Valley. Knight Valley has five main areas with a seafront waterfall, while Tea Stream Resort Valley offers four themed areas including an Ancient Tea Town, Interlaken, Wetland Garden, and Sanzhou Tea Garden. Each area provides unique experiences, such as wine tastings, water golf, indoor tennis, and traditional Chinese culture performances.
Discovering Chuanlord Manor During Chinese New Year in GuangDong China
Chuanlord Manor in GuangDong, China, offers an unusual theme park experience with animal attractions during Chinese New Year. The park features various rides, including gentle children's rides and intense coasters like the Dragon & Phoenix Coaster. Animal shows, interactive experiences, such as feeding fish or tossing rings around ducks, make it a fun destination for families.
Golden Splendor and Ancient Whispers at Shwedagon Pagoda in Yangon Myanmar
Shwedagon Pagoda in Yangon, Myanmar is one of Buddhism's most sacred sites, featuring 27 metric tons of gold leaf and thousands of diamonds. The pagoda is believed to enshrine eight hairs of the Gautama Buddha and has been rebuilt many times due to earthquakes, with the current structure dating back to the Bagan period (10th-14th centuries).
A Visit to the Ulaanbaatar National Museum of Mongolia
The National Museum of Mongolia in Ulaanbaatar is one of the country's national museums, established in 1924. It features exhibits on Stone Age sites, petroglyphs, and burial sites, as well as a collection of costumes, hats, jewelry, and traditional Mongolian culture. The museum also houses real examples of 12th-century Mongol armor, correspondence between Pope Innocent IV and Guyuk Khaan, and artifacts from D Sükhbaatar's life, including his famous hollow horsewhip.
Life is like a camera. Just focus on what's important and capture the good times, develop from the negatives and if things don't work out, just take another shot. - Unknown
Secret Garden Skiing Resort Ski Destination of Olympic Territory in Beijing China
Genting Secret Garden Ski Resort in Beijing, China offers a range of slopes for all skill levels, including easy green runs, double black diamonds, and heated gondolas. The resort features amenities such as pool tables, foosball, and an island cocktail bar with live music. It's part of the larger 2022 Winter Games venue, built on a $6.5 billion investment with six new venues and reuse of existing ones to meet IOC goals for affordability.
Lotte World: A Year-Round Extravaganza of Fun in Seoul South Korea
Lotte World Seoul is an all-year-round theme park open until 10pm or 11pm, depending on weekdays or weekends. It features indoor areas to escape bad weather and various thrill rides, including roller coasters like Atlantic Adventure and Flume Ride. The park also celebrates festivals, such as Halloween, with decorations, performances, and characters. Rides offer scenic views of the park via the World Monorail and Aeronauts Balloon Ride.
The Wonders of Chimelong International Circus in Guangzhou China
The Chimelong International Circus China is located within Guangzhou Chimelong Holiday Resort and features an impressive lineup of top circus performers from around the world, including over 1,000 animal stars. The show "New Forest Code" has already received great success both critically and commercially, showcasing high-tech special effects and vivid background settings that bring a new experience to audience members.
From Kung Fu Panda Academy to Water Wonders: Family Fun in Macau
The Kung Fu Panda Academy at the Sheraton Hotel in Macau features an interactive obstacle course with five zones that challenges children's physical abilities and problem-solving skills. Upon completion, they receive a Kung Fu-themed goodie bag and can take photos with Po for a photo shoot. The Junior Hotelier program allows kids to learn hotel operations while having fun, teaching them various roles such as chef, barman, or housekeeper.
Tap Mun: A Tranquil Escape to Grass Island in Hong Kong
Tap Mun Island is a 1.7sq km grassy island off the coast of Sai Kung Country Park, home to Hakka and Tanka people and popular for camping and kite-flying. A 2km footpath offers panoramic views and a refreshing breeze before ending at a seafood restaurant where you can try local specialties like ice-less iced milk tea. The island features ancient temples, an abandoned school, and pirate tunnels among its attractions.
Chimelong Ocean Kingdom World-Class Marine Wonderland in Zhuhai China
The Chimelong Ocean Kingdom aquarium in Zhuhai, China features a large aquarium with whale sharks, beluga whales, dolphins, and other marine animals. It has been ranked as the world's largest aquarium with 48.75 million liters of water, offering various shows, including submarine rides and dolphin performances, as well as nighttime firework displays on a central lake.
From the DMZ Solemnity to Snowy Slopes at Alpensia Ski Resort in Kangwon South Korea
The blog post describes a trip to South Korea during Chinese New Year holiday. The author visited several sites in the Demilitarized Zone (DMZ), including Imjimgak, Dora-san Observatory, Panmunjom, and the 3rd Tunnel. They also spent time at COEX Aquarium and Alpensia Ski Resort, enjoying various attractions such as fish tanks, moving walkways, and snowboarding for kids. The family had a fun experience with skiing lessons and creating giant snowmen.
The intention of a photgrapher is to capture the beauty in places, obvious or hidden, in which modern age and technology cause us to dismiss. - Kassadi Collins
Winter Wonderland and Culinary Delights at Secret Garden Skiing Resort in Beijing China
Genting Secret Garden Resort, located near Zhangjiakou City, offers a range of slopes for all skill levels and features modern amenities like heated gondolas and comfortable facilities. The resort also hosts a bar with live music performances and an in-house restaurant serving Chinese cuisine. It's part of a joint bid to host the 2022 Winter Olympics alongside Beijing, with transportation between the two cities planned via high-speed railway.
A Fun Soccer Tournament at Clear Water Bay Hong Kong
The Asia Pacific Soccer Schools held a Fun Soccer Tournament at Clearwater Bay Golf & Country Club in December 2014 for non-squad members. Eight teams competed in each age group, with players randomly assigned to teams before the tournament began. The event was a fun opportunity for participants to play soccer near Christmas.
Disney Paint the Night Parade in Hong Kong
The Disney Paint the Night parade features a colorful display of light and color at Hong Kong Disneyland Park. Mickey transforms the park into his "canvas" with pixie-dust infused lights and decorations. Favorite characters, including Tinker Bell, Ariel, Belle, and Buzz Lightyear, join in the celebration, adding to the enchanting atmosphere.
Riding the Waves of History: The Santa Cruz Surfing Museum in California
The Santa Cruz Surfing Museum is located in a converted lighthouse overlooking Steamer's Lane, showcasing the history of surfing in Santa Cruz. The museum features a small collection of surfboards, including wooden and fiberglass models, as well as exhibits on the light's construction and relocation due to erosion. Admission is free, with optional donations to support the museum.
Wonderful Harvest Fair Pumpkins in the Park in San Jose
Pumpkins in the Park is a harvest fair promoting environmental awareness and celebrating the fall season at Guadalupe River Park in San Jose, raising funds for its conservancy. It also features visits to the Cathedral Basilica of St. Joseph, a historic landmark with Greek cross ground plan, and the Rosicrucian Egyptian Museum, housing the largest collection of Egyptian artifacts on exhibit in western North America.
Fleet Week Air Show: A Spectacle of Seaborne and Aerial Power in San Francisco California
Fleet Week in San Francisco features active military ships docked in the city for a week, allowing crew members to visit tourist attractions and take guided tours of the ships. The event is accompanied by air shows, including performances by the Blue Angels on October 11-12, 2014, featuring six Navy fighter planes performing precision flying stunts over San Francisco Bay.
Wings of History Air Museum: A Haven for Aviation Enthusiasts in Gilroy California
The Wing of History Air Museum in Gilroy, California, is a nonprofit organization dedicated to preserving and restoring antique aircraft since 1974. The museum features over 100 historic planes, including replicas and original models by renowned designers like Burt Rutan and Volmer Jensen, with many displays labeled with historical notes on their manufacture and significance. Volunteers actively restore and maintain the collection, which also includes a library and prop shop.
The Princess and the Nutcracker: Petite Princess Academy Showcase
Petite Princess Academy of Dance organized a 2014 annual dancing performance called "The Princess and the Nutcracker." The school provides training in various exams, including RAD, ATOD, and CSTD. Serena, who had been practicing for 3 months, participated in the performance, which she did well.
National Martyrs' Memorial in Bangladesh
The National Martyrs' Memorial in Bangladesh was designed by Syed Mainul Hossain and inaugurated in 1982. It commemorates the valour and sacrifice of those who fought for Bangladesh's independence from Pakistan in 1971. The monument features 7 triangular pyramid-shaped structures, an artificial lake, and mass graves, standing at 150 feet high with several facilities and structures nearby.
Exploring Bustling Markets, Cultural Oasis, and Playful Discoveries in Tokyo Japan
We visited Ameyoko Shopping Street in Ueno, Tokyo, for its cut-price shops selling seafood, clothing, and more. We also explored Ueno Park, featuring multiple museums, the National Zoo, and over 1,000 cherry trees with stunning blooms. The park is home to Ueno Toshogu Shrine, a historic shrine dedicated to Tokugawa Ieyasu, and hosted a Botan Festival featuring peony flowers.
An Adventure in the Heart of Tokyo: Exploring Ueno Zoo in Tokyo Japan
The Ueno Zoo in Tokyo, Japan is a 35-acre zoo managed by the Tokyo Metropolitan Government. It's home to over 2,600 individuals of 460 species, including rare animals like the Ruddy Kingfisher. The zoo was without giant pandas for the first time since 1972 until two new pandas arrived in 2011 from the Chinese Wolong Nature Reserve, and has undergone significant changes with modern habitats replacing old cages.
Stepping into a World of Kawaii: Entering Sanrio Puroland in Tokyo Japan
Sanrio Puroland is a theme park located in Tama, west of Tokyo, featuring popular Japanese characters like Hello Kitty, My Melody, and Cinnamoroll. The park offers various attractions, shows, and exhibits, including a boat ride and live theaters, with a focus on Sanrio goodies and merchandise. It's a popular destination for families and fans of the brand, with many overseas visitors drawn in by its worldwide popularity.
A Nautical Journey Through Fantasy at Tokyo DisneySea in Tokyo Japan April 2014
Tokyo DisneySea is a 176-acre theme park at Tokyo Disney Resort with 7 uniquely themed areas. The Mediterranean Harbor serves as the entrance, featuring Venetian Gondolas, while Mermaid Lagoon and Arabian Coast are popular attractions for families, inspired by Disney's The Little Mermaid and Aladdin, respectively. The park offers various rides, shows, and experiences, including Fantasmic! and nighttime spectaculars.
Dubai Delights: From Marina Lights to Desert Nights in Dubai UAE
The author visited various attractions in Dubai, including a sunset cruise on the Marina, the Dubai Museum in Al Fahidi Fort, the Gold Souk, Burj Al-Arab hotel, Desert Safari, and Burj Khalifa. Highlights included the thrilling 4x4 desert ride, camel ride, and live belly dance performance, as well as the elevator ride to the top of Burj Khalifa for breathtaking views.
Exploring Fujairah: A Journey Through History, Nature, and Coastal Charm in Fujairah UAE
Fujairah is a historic city in UAE known for its rich marine environment and archaeological finds dating back to the Iron Age. The Al Badiyah Mosque, the oldest known mosque in the UAE, and the 360-year-old Al Bithnah Fort are notable attractions. Visitors can also explore the Fujairah Heritage Village, Snoopy Island with its excellent snorkeling opportunities, and stop at Friday Makret for local fruits, handicrafts, and souvenirs along their route to Dubai.
Oasis History, Palaces, and Camelicious Delights in Al Ain UAE
Al Ain, UAE is an oasis city 140Kms from Dubai, featuring ancient archaeological sites like Hili Archaeological Park, which dates back to the 3rd millennium BC. The Sheikh Zayed Palace Museum showcases traditional Emirati life, while the Al Ain National Museum offers a 7500-year history of UAE culture and traditions. Visitors can also explore the Al Nassma Camel Farm, where they can feed and pet camels, including those producing camel milk chocolate, a unique taste experience in the region.
Contrasts in Phnom Penh: Royal Grandeur and Somber Remembrance in Cambodia
The Royal Palace in Phnom Penh is a 500x800 meter walled complex serving as the residence of King Norodom Sihamoni and former King Sihanouk. The grounds also house the 'Silver Pagoda' compound, open to the public except during official functions, with admission at 25,000 Riel (US$6.25). In contrast, Choeung Ek, a 17 km south site known as "The Killing Fields", marks the mass graves of over one million Khmer Rouge victims.
Angkor Wat: Witnessing History and a Legendary Sunrise in Siem Reap Cambodia
Angkor Wat is an ancient temple complex in Cambodia that was built in the first half of the 12th century during the reign of Suryavarman II. Dedicated to Vishnu, it was originally designed as the king's state temple and capital city but later moved to Hindu and Theravada Buddhist use. The site was declared a UNESCO World Heritage site in 1992 and is still preserved today due to its moat providing protection from jungle encroachment.
Marine Wonders, High-Flying Acrobatics, and Nostalgic Charm at Aqua Voyage Ocean Park in Hong Kong
Ocean Park Hong Kong features animal exhibits, thrill rides, and shows. The Aqua Voyage aerial spectacular promotes marine conservation with a story about a young girl discovering an underwater world, accompanied by performances from top performers. Visitors can also explore the Old Hong Kong street, a replica of the old town, and experience attractions like the Polar Adventure, which showcases polar animals such as walruses and arctic foxes.
We try to grab pieces of our lives as they speed past us. Photographs freeze those pieces and help us remember how we were. We don't know these lost people but if you look around, you'll find someone just like them. - Gene McSweeney
A Bricktastic Adventure: Discovering Legoland Johor Bahru in Malaysia
Legoland Malaysia is a theme park in Nusajaya, Johor, Malaysia with over 40 interactive rides, shows, and attractions. The park features Lego-themed areas like Kid Power Towers, Castle Hill, and Miniland, which showcases Asian landmarks built from Lego bricks. The park also offers activities like building, robotics, and aerial monorail rides, making it suitable for children aged 2-10.
Hello Kitty Town and The Little Big Club in Johor Bahru Malaysia
The blogger visited Hello Kitty Town in Johor Bahru, Malaysia, as part of a package deal with Little Big Club. The park features interactive activities, rides, and performances centered around Hello Kitty, as well as character play areas like Barney's and Thomas & Friends' zones. Admission costs RM85 for foreigners and RM110 for Malaysians, with reasonable food options available on both levels.
Experiencing the Magic of Universal Studio Singapore
Universal Studios Singapore opened in December 2006 as part of Resorts World Sentosa on Sentosa Island. The park has attracted over 2 million visitors since its opening, featuring popular rides like the Transformer ride, Lights, Camera, Action!, and Madagascar. It is the second Universal Studios theme park in Asia and the first in Southeast Asia, offering a unique experience with advanced special effects and immersive scenes.
Beneath the Surfac Journey Through the S.E.A. Aquarium in Singapore
The SEA Aquarium Singapore features over 100,000 marine animals from 800 species in 45 million liters of water across 49 habitats. It boasts a world-record viewing panel measuring 36 meters wide and 8.3 meters high. The aquarium showcases diverse marine life, including dolphins, sharks, rays, jellyfish, and various fish species, making it a spectacular collection with excellent staff service, highly recommended for visitors.
Gardens by the Bay: A Botanical Oasis in Singapore
Gardens by the Bay is a 101-hectare park in Singapore featuring three waterfront gardens: Flower Dome and Cloud Forest. The Flower Dome replicates Mediterranean climate and features plants from Australia, South America, and Africa, while the Cloud Forest mimics tropical mountain regions with cool moist conditions. Both feature unique structures and displays, including the Flower Dome's 38m-high dome and Cloud Forest's 42m-high Cloud Mountain with an elevator access.
Navigating the Singapore Zoo During the Holidays in Singapore
The Singapore Zoo offers a good experience with its variety of 315 species of animals, including threatened ones. Shows like "Rainforest Fights Back," "Elephants at Work and Play," and "Animal Friends" are worth seeing. The zoo is operated by Wildlife Reserves Singapore and managed along with the Night Safari and Jurong BirdPark. Tickets can be booked ahead to avoid long waits during peak season, but may take over an hour to secure a time slot due to popularity.
Exploring the Hong Kong Railway Museum in Hong Kong
The Hong Kong Railway Museum is a 1985 railway museum in Tai Po, managed by the Leisure and Cultural Service Department. It's located at the site of the Old Tai Po Market Railway Station, built in 1913, and features exhibits on KCR trains, Japanese Shinkansen, Eurostar, as well as historic locomotives like "Sir Alexander" (1955) and a narrow gauge steam locomotive from the Philippines (restored in 1995).
Cruising the Danube and Uncovering History in Budapest Hungary
The article describes a blog about visiting Budapest, Hungary's capital city, with several UNESCO World Heritage Sites. The author recounts their experiences cruising on the Danube River, exploring the Parliament building, Fishermen's Bastion, Heroes' Square, and Citadella at Gellért Hill, enjoying traditional Hungarian cuisine and entertainment along the way.
Historic Zagreb and the Emerald Waters of Plitvice Plitvice Lakes National Park in Croatia
This text describes Zagreb, the capital city of Croatia, and Plitvice Lakes National Park, highlighting their cultural and natural significance. Zagreb boasts a charming medieval old town with a cathedral dating back to 1093, while Plitvice Lakes National Park is known for its stunning natural beauty, featuring 16 interconnected lakes and a vast forest complex.
Fairytale Castles, Enchanting Lake Bled, and Underground Wonders in Slovenia
The Bled Castle in Slovenia offers panoramic views, a restaurant, and a small café. The island in the middle of Lake Bled, where the castle stands, has several buildings, including a pilgrimage church dedicated to Mary. According to legend, a young widow had a bell cast for the chapel that sank during transport, only to be replaced by a new one blessed by the Pope, which is said to grant wishes to those who ring it.
Austria's Alpine and Imperial Wonders: Hallstatt, Salzburg, and Vienna in Austria
The blog describes a trip to Austria, visiting Hallstatt and Salzburg. Hallstatt has breathtaking views and is a UNESCO heritage site with an old cemetery dating back to the early Iron Age. In Salzburg, the author visited Mozart's Geburshaus museum, the Makartsteg bridge, Mirabella Gardens, and Vienna's historic center, including Baroque castles and gardens, the Stadtpark, and iconic landmarks like Strauss' statue.
Unlocking Czech History: Prague, Castles, and South Bohemian Towns in Czech Republic
We visited Prague Castle in St. Vitus Cathedral, a Gothic masterpiece, and explored the city's picturesque Lesser Town, Charles Bridge, and Old Town Square. We also stopped at Karlovy Vary for spa treatment and visited Cesky Krumlov castle, which offers stunning views of the surrounding hills and river. Additionally, we toured Ceske Budejovice, known for its brewing history and historic town center with notable landmarks such as the Black Tower.
Berlin, Dresden, and the Bastei: Diverse Experiences in Germany
The blog describes a visit to Berlin and Dresden, Germany, exploring landmarks like the Brandenburg Gate, Deutsches Historisches Museum, Kaiser Wilhelm Memorial Church, and Checkpoint Charlie. The author also visited Dresden's Theaterplatz, featuring the Zwinger Palace, Semper Opera House, and Italian Dörfchen. Finally, they stopped by the Bastei rock formation near the Czech border, learning about its geological history.
Escape to Shenzhen's Alpine Wonderland at Shenzhen Overseas Chinese Town East in China
OCT East, a Swiss Mountain Resort in Shenzhen's Dameisha, features two theme parks: Ecoventure Valley and Tea Stream Resort Valley. The resort includes five main theme areas with attractions like the Giant Waterfall and a 300-room hotel with an Austrian chef. Developed at $450 million, the park aims to offer a European taste of China, complete with antique railroad tours and yodelers, leaving guests believing they are indeed in Europe.
Piece of Peace Lego Exhibition in Hong Kong
A "Piece of Peace" Lego Exhibition was held in Hong Kong in July 2013, showcasing miniature Lego models of cultural legacies from 25 countries, including Chinese World Heritage sites. Created by Hong Kong Lego builders, these replicas were part of the exhibition alongside previously displayed pieces. This event follows a successful series of exhibitions started in Japan in 2003, which has attracted over 1.5 million visitors worldwide.
Welcomes a Giant Dose of Joy: The Arrival of the Rubber Duck in Tsim Sha Tsui Hong Kong
The World's largest rubber duck, created by Dutch artist Florentijn Hofman in 2007, measures 16.5 x 20 x 32 meters and weighs over 600 kg. The giant inflatable duck is part of Hofman's "Spreading joy around the world" tour, designed to evoke childhood memories, and has been displayed in various countries before arriving in Hong Kong on June 9, 2013.
A Taste of Venice in Macau: Experiencing The Venetian Macao and its Italian Carnevale in Macau
The Venetian Macao is a luxury hotel and casino resort in Macau owned by Las Vegas Sands. It features a 40-story building with over 10 million square feet of space, modeled after its sister resort in Las Vegas. The property hosts the annual Venetian Carnevale celebration, offering Italian-themed entertainment, street performers, and game booths, with proceeds benefiting charity.
Celebrating Our Twin Fantastic 5th Birthday at the Party
The author organized a twin 5-year-old birthday party, hiring a clown to entertain the kids. The clown performed body/arm painting, balloon twisting, and sculpting, making the party a joyful and memorable event for friends and family.
Discovering Faith, Nature, and Fun at Noah's Ark in Ma Wan Hong Kong
Noah's Ark on Ma Wan Island in Hong Kong opened in 2009 as a tourist attraction blending nature, art, education, and love. The park features a full-size Noah's Ark simulation with sculptures of animals, birds, and creatures exiting the ark. It also includes an obstacle course, climbing, reptile display cages, and a nature garden alongside the existing natural landscape, catering to young children and adventure-seekers alike.
Easter Adventures in Guangzhou with the Twins: Museums, Markets, and Merriment in China
The author visited Guangzhou, China with their twin children during Easter holiday. They explored the Guangdong Museum, which features over 166,000 items including fossils and dinosaur exhibits, and the Guangzhou Library, designed by Japanese firm Nikken Sekkei. The family also spent time at the Canton Place Easter Carnival, the Guangzhou Zoo, where they saw a seal/dolphin show, and the Zhujiang Park, where children fed fish with bread.
A Sprinkle of Pixie Dust: Meeting Tinker Bell at Hong Kong Disneyland Pixie Hollow
Pixie Hollow is a character meet and greet attraction at Disneyland Hong Kong featuring Tinker Bell. She is a small, feisty, and beautiful fairy with blue eyes, blonde hair, pointy ears, and fair skin. Her personality varies greatly, ranging from hot-tempered to helpful and kind, due to the limitations of her fairy size which prevents her from holding multiple emotions at once.
Dawan Residence in Pingshan China
The blogger visited a military theme park in Shenzhen, Minsk World, which features a recreated Soviet aircraft carrier. Nearby, they explored The Dawan Residence, a 1791 fort square Hakka site in Longgang district. The residence was designated as a protected historical site for its cultural significance and has remnants of firecrackers from the Chinese New Year celebration.
Navigating the Lunar Rush: A Family Adventure at Netherlands Flower Town in Shenzhen China
The blog visited the Netherlands Flower Town in Shenzhen, China, where they enjoyed Dutch historical buildings and flower exhibitions at wholesale prices. They also spent time at the Guangdong Science Center, exploring science and technology exhibits, before visiting the Long Deer Farm Resort & Theme Park for roller coaster rides and animal performances suitable for young kids and families.
Fashion, flowers, nudes and portraits - they're all the same: light, form, color. And mystery. And mystery is very important. When I started photographing flowers, I thought, "My God, where have I been?" I'm totally addicted to this project. I'd never seen the mysteries of a flower. We walk by wonders every day and don't see them. We only stop at what shouts the loudest. - Barbara Bordnick
Fun and Animals at Leofoo Village Theme Park Hsinchu in Taiwan
Leofoo Village Theme Park in Guanxi, Hsinchu, Taiwan features 4 distinct zones: Wild West, South Pacific, Arabian Kingdom, and African Safari. The park offers various attractions, including animal-interactive experiences like feeding goats and riding horses. Thrill seekers can enjoy the Ring of Fire, Screaming Condor, and Old Oil Well rides. With unique characteristics in each zone, it's a great destination for families and young at heart.
A Day with the Animals: Exploring the Expansive Taipei Zoo in Taiwan
The Taipei Zoo in Taiwan was founded in 1914 as a private garden owned by a Japanese citizen. After WWII, it passed to the Taipei city government and moved to its current site in Muzha in 1986. The zoo features 165 hectares of enclosures, including open areas and various animal exhibits, such as giant pandas, giraffes, zebras, bears, and penguins, with a train system for easy navigation.
Experiencing Job Simulation City During Christmas at BabyBoss Taipei in Taiwan
The writer visited BabyBoss City, Taiwan's first simulation city, with their twin children during Christmas holidays. The 2300 sq. city features over 70 occupations for kids to explore, promoting learning and fun through games and role-playing scenarios. They also dined at a Hello Kitty-themed restaurant, where they enjoyed desserts and a set menu with beverage, soup, appetizer, and dessert, with a minimum spending requirement of NT300 per person.
Discovering the Wild West Charm of Grizzly Gulch at Disneyland Hong Kong
Hong Kong Disneyland's new Grizzly Gulch area opened in July with an authentic Wild West theme. Inspired by California's Sierra Nevada Mountains, the area features attractions like Big Grizzly Mountain Runaway Mine Cars, Mother Geyser, and Bear Necessities. The area also includes shopping and meet-and-greet opportunities with Disney friends. A new themed area, Mystic Point, is set to open next year in a dense rainforest setting.
Little Professionals at Work: Exploring EE City Job Simulation in Beijing China
EE City is a simulation city in Beijing designed for children aged 4-15, allowing kids to play and learn through various occupations and role-playing scenarios. Children earn money, value its worth, and make purchases, teaching them valuable life skills. The facility features multiple settings, including jobs like police officer, doctor, and airline pilot, which stimulate learning capability and provide an enjoyable experience for children.
Making Memories at Hong Kong Disneyland Mickey Mouse in Hong Kong
The Hong Kong Disneyland theme park offers various magical experiences, including Broadway shows, 3D movies, and iconic attractions like "Buzz Lightyear's Astro Blasters" and "It's a Small World". Visitors can take the MTR to Sunny Bay station and then the Disney train to reach the park. Photo opportunities with beloved characters like Mickey Mouse and Minnie are also available, making it a must-visit destination for families.
A Feathered Paradise: Exploring the Wonders of Jurong Bird Park in Singapore
Jurong Bird Park in Singapore features over 8,000 birds from 600 species on 20 hectares of lush greenery. The park offers various shows and exhibits, including the African wetlands with native-style pavilions, as well as amenities like eateries, a train tour, and water play areas for children. With neatly maintained grounds and no trash, it provides a pleasant experience despite high visitor numbers.
A Deep Dive into the Ocean at Underwater World Singapore Singapore
The Underwater World is an oceanarium on Sentosa Island in Singapore, opened in 1991 with over 2,500 marine animals from around the world. It features an 83m long underwater corridor where kids can interact with rays and sharks, as well as a dolphin lagoon with live performances. The oceanarium also supports environmental and educational projects through various programs.
Easter Fun in Singapore: Island Living and a Nocturnal Adventure at Sentosa Island in Singapore
The blogger visited Sentosa Island in Singapore during Easter 2012 with their twin. The island was developed with a $420 million private investment and $500 million government funding, featuring attractions like Fort Siloso, Musical Fountain, and Underwater World. They enjoyed the Night Safari, a nocturnal zoo that allowed them to observe animals under the moonlight from the tram for a unique experience suitable for families with small children.
A Blooming Spectacle: Reveling in the Hong Kong Flower Show
The Hong Kong Flower Show 2012 was held at Victoria Park from March 16-25 with a "Hyacinth" theme and "Floral Delights." Over 200 organizations from 21 countries showcased exotic flowers, landscape displays, and floral art, including Mainland China, Australia, Canada, and the United States. Fringe activities included music performances, green talks, fashion shows, cooking demos, and games.
I enjoy traveling and recording far-away places and people with my camera. But I also find it wonderfully rewarding to see what I can discover outside my own window. You only need to study the scene with the eyes of a photographer. - Alfred Eisenstaedt
A Christmas with Wild Encounters and Floral Fantasies at Songshan Lake Industrial Park in China
The writer visited the Chimelong Xiangjiang Safari Park in Guangzhou, China, during their Christmas vacation tour. The 130-hectare zoo is home to over 20,000 animals from 450 species, including endangered international species like white tigers and pandas. They opted for the "Safari on Foot" route, enjoying a more relaxed experience amidst many species, and plan to return with their twin child soon.
Shrunk to Toy Size: Exploring Hong Kong Disneyland's Toy Story Land in Hong Kong
Toy Story Land opened in Hong Kong Disneyland Resort in December 2011, featuring themed props, characters, and a gentle ride called Slinky Dog Zigzag Spin suitable for young kids. The area's theming and music are praised, making it an attractive addition to the park. It's not exclusive to Hong Kong, as a similar area is found at Walt Disney Studios in Paris, but will also be built at Shanghai Disneyland.
Venetian Grandeur, Kid-Friendly Fun, and Delicious Local Bites at Venetian Resort Hotel in Macau
The Venetian Hotel in Macau features a Kid's Zone area called Qube, designed for children aged 4-17 with play equipment like multi-climbing facilities, slides, and video games. The hotel also has an on-site restaurant, Cozinha Pinocchio, serving traditional Portuguese dishes that taste wonderful, including grilled pork, fried rice, spaghetti, and curried chicken.
A Mosaic of China: Exploring the Rich Cultures at China Folk Cultural Village in Shenzhen China
China Folk Cultural Village in Shenzhen features life-size replicas of 24 villages from ethnic groups across China, showcasing folk arts, customs, and residential buildings. The village offers various performances, including traditional dance and music, local snacks, handicrafts, and souvenirs. Visitors can enjoy live shows daily, such as Uygur women twirling to Turkish music or a Tibetan rock band, making it a highly recommended cultural experience in Shenzhen.
The Iconic Sands of Haeundae: A Busan Beach Experience at cHaeundae Beach in Busan South Korea
The Haeundae Beach in Busan, Korea is one of the country's most famous beaches, named after scholar Choi Chi-Won who left carved words on a stone wall in 857 AD. The beach stretches 1.5 km long and spans an area of 58,400㎡, featuring white sand and shells eroded by wind over time. It hosts various cultural events and festivals throughout the year, with traditional games and activities available at the Folk Square and Beach Library.
Exploring Ancient Gyeongju, Capital of Silla at Bulguksa Temple in Busan South Korea
We visited Bulguksa Temple in Gyeongju, South Korea, an Unesco World Heritage Site built in 535 by King Pob-hung for his queen to pray for the kingdom's welfare. The temple was destroyed and partially rebuilt during Japanese occupation and fully restored under President Park Chung-hee. Today it is home to seven Korean national treasures and features a large water wheel called Bomun Mulebanga, symbolizing mental clarity and fulfillment of dreams.
Exploring Busan: From Bustling Markets to APEC History in Busan South Korea
Gukje Market is a historic marketplace in Busan, South Korea, that originated during the Korean War as a refuge for war refugees. Today, it features an assortment of new and used items sold at low prices by vendors who also deal with wholesale sales. The market is near other popular tourist attractions like Bupyeong Market and Nurimaru APEC House, a modern building inspired by traditional Korean architecture that hosted the 2005 APEC Summit Talks.
Danshui Escape: Sunsets, Seafood, and Historic Eats at Fisherman's Wharf in Taiwan
Danshui Fisherman's Wharf in Taiwan is a small fishing city with a romantic atmosphere, attracting couples who come to watch sunsets and stroll along the Lover's Bridge, a 196-meter cable-stayed bridge built for Valentine's Day in 2003. The wharf has undergone renovations, featuring new buildings, restaurants, and shops, including a lively Old Street with night markets serving delicious Taiwanese snacks until late at night.
Grand Memorials and the Capital of Tofu Around Chiang Kai-Shek Memorial Hall in Taipei Taiwan
Chiang Kai-Shek Memorial Hall features a museum on its ground floor with exhibits on the former Taiwanese president's life, including his military uniforms and cars. A gigantic bronze sculpture of Chiang sits at the top of 89 steps, flanked by motionless guards. The hall is also known for its strict dress code, stating that those wearing slippers or slovenly clothing will not be admitted.
Experiencing the Flights of Fantasy Parade at 5th Aniversary DisneyLand Hong Kong
The Hong Kong Disneyland Flights of Fantasy Parade celebrates the 5th anniversary of the park with eight floats featuring beloved Disney characters. The parade includes themed floats such as Mickey's Magical Airship, Pooh's Dreamship, and Toy Story's To infinity and beyond ship, which showcases Woody, Jessie, and Ham from the Toy Story movies.
A Wild Day Out at Shenzhen Safari Park in China
Shenzhen Safari Park, located in Xili University District, offers over 300 breeds of animals, including rare species like pandas and Siberian tigers. Tickets cost 130 RMB per adult, with free admission for children. Visitors can walk around or take a horse-drawn carriage ride for an additional fee to see various exhibits, including the Elephants and Tigers Show Hall featuring tiger and lion performances.
Celebrating Our Twin Three Years Oldd Special Birthday
A blog post commemorates a twin 3-year-old's birthday party held in May 2011. The author reminisces about their previous year's successful 2-year-old party, welcoming friends and kids to celebrate another joyful event. They express gratitude to guests who attended and shared the happy moment.
A Frightening Health Scare and the Joys of Toddlerhood in Hong Kong
The author's twin sons had a terrifying experience with febrile seizures caused by flu viruses, which left them unconscious and in seizures for a few minutes. Fortunately, the fever subsided after 5 days of hospitalization, and the boys are now recovering well, enjoying school, dress-ups, and playtime. They express themselves through words and sentences, showing significant development at their age.
Photography is a system of visual editing. At bottom, it is a matter of surrounding with a frame a portion of one's cone of vision, while standing in the right place at the right time. Like chess, or writing, it is a matter of choosing from among given possibilities, but in the case of photography the number of possibilities is not finite but infinite. - John Szarkowski
Magical Moments and Toddler Triumphs at Hong Kong Disneyland
The writer visited Hong Kong Disneyland for the second time, bringing their 2.5-year-old twins along. They enjoyed shows like "It's a Small World" and "Winnie the Pooh," but found some attractions too loud for young children. The trip was successful despite crowded trains, and they plan to return next year with more photo opportunities and magical experiences.
Beijing During National Holiday: A Family Adventure Through Wildlife, Markets, and Celebrations in China
The blogger visited Beijing Zoo with their family, including twins, during China's National Holiday. The zoo features over 7,000 creatures from around the world, including giant pandas, giraffes, and elephants, at an affordable entrance fee of RMB15 per person. Afterward, they explored Wang Fu Jing Avenue and Quan Ju De for lunch, and attended a wedding ceremony with panoramic views from the CCTV Tower's observation deck.
Watching Our Twins Explore and Blossom at Two Years 1 Month Old
Two-year-old twins exhibit curiosity and explore their surroundings daily. They make connections with peers and demonstrate new skills such as communication and independence. Unique personalities start to emerge, with one daughter becoming shy initially but warmening up quickly, while the son is energetic and active. Each twin excels in certain areas, showcasing distinct traits.
The blog visits three main attractions: A-ma Temple, a 500-year-old temple dedicated to Tin Hau; Chapel of Our Lady of Penha, rebuilt in 1837 after its initial construction in 1622; and the Venetian Macao, a $2.4 billion casino resort with a 40-story hotel, featuring the largest single structure hotel building in Asia.
Ocean Park Hong Kong: A Story of History, Heart, and High Attendance in Hong Kong
Ocean Park in Hong Kong opened in 1977 as a subsidiary of the Hong Kong Jockey Club, initially funded by the government's donated land. It became an independent body in 1987 and experienced a decline until recent years, when attendance soared to break records multiple times, with mainland Chinese visitors accounting for 53% of visitors since 2011. The park now attracts 7.1 million visitors annually and has doubled in size through a HK$5.5 billion expansion program.
Exploring the Lions Nature Education Centre in Sai Kung Hong Kong
The Lions Nature Education Centre in Sai Kung, Hong Kong features 34 hectares of land with various outdoor display areas, including an insectarium, pond, shell house, and gardens featuring crops, medicinal herbs, and trees. The centre offers public education, recreational activities, conservation, and scientific studies, showcasing a variety of plants and animals for educational purposes.
Visiting the the Tokyo National Museum and a Master Painter in Tokyo Japan
The Tokyo National Museum is Japan's oldest national museum, established in 1872, with over 110,000 objects in its collection. The museum includes galleries featuring Japanese art and Asian artifacts, as well as restaurants and shops. A special exhibition gallery was on display in 2010, showcasing the works of Hasegawa Tohaku, a renowned painter from the Momoyama period, whose masterpieces are considered national treasures.
A Glimpse of Edo Grandeur: Exploring Ueno Toshogu Shrine in Tokyo Japan
Toshogu Shrine in Ueno Park, Tokyo, is dedicated to Tokugawa Ieyasu and dates back to 1651. The shrine has survived various disasters, including wars, earthquakes, and bombings, retaining its original glory with gold and green roof and luxurious walls. It features intricate carvings of dragons, flowers, and birds on the gates and corridors, as well as beautiful paintings on its walls and ceilings.
Finding Peace and History at Meiji Shrine in Tokyo Japan
Meiji Shrine is a Shinto shrine dedicated to Emperor Meiji and Empress Shoken, located in Tokyo's densely built-up area. Completed in 1920, the shrine was destroyed during WW2 but rebuilt shortly after. It features traditional Japanese architecture and offers a peaceful stroll through its grounds, which also host Shinto wedding ceremonies and offer great photography opportunities.
Ueno Park Cherry Blossom in Tokyo Japan
Ueno Park in Tokyo's oldest and largest park, covering 533,981 sqm with over 8,650 trees and 86,800 shrubs. Originally built to guard Edo Castle, it was opened to the public in 1873 and granted to the city of Tokyo by Emperor Taisho in 1924. The park is a popular spot for hanami during cherry blossom season (late March to early April) with family activities, museums, a zoo, concert hall, pond, shrines, and monuments.
A Garden of Wonders at the Hong Kong Flower Show
The Hong Kong Flower Show 2010 was held at Victoria Park from March 19-28, attracting over 538,000 visitors. The theme flower was Cineraria, with a "Fairy Tales of Flowers" theme, featuring about 200 organisations from 21 countries showcasing exotic flowers and floral art displays. Fringe activities included music and dance performances, fashion shows, cooking demonstrations, green talks, and games.
From Grand Monuments to Historic Harbors and Vibrant Chinatown in Jakarta Indonesia
Jakarta, Indonesia's capital, has a rich history dating back 490 years. The city boasts unique monuments like the National Monument, a 132m tall phallic symbol representing the nation's strength and independence. Glodok, a Chinese-ambiance area, offers colorful shops, markets, and temples, while Sunda Kelapa, near Old Batavia, features historic sailing ships providing spectacular views of Jakarta's bustling streets.
Nearing Two: A World of New Skills and Boundless Curiosity for Our Twin Babies
Twin babies are now 1 year 9 months old, with increasing independence and curiosity. They walk confidently and explore their surroundings with energy, often picking up small objects and putting them in their mouth. Play has been an essential part of their learning experience, helping them understand predictability and cause-and-effect relationships. Establishing routines has also helped the twins feel secure and more manageable for parents.
The personality and style of a photographer usually limits the type of subject with which he deals best. For example Cartier-Bresson is very interested in people and in travel; these things plus his precise feeling for geometrical relationships determine the type of pictures he takes best. What is of value is that a particular photographer sees the subject differently. A good picture must be a completely individual expression which intrigues the viewer and forces him to think. - Alexey Brodovitch
Discovering Wildlife Wonders at Chimelong Safari Park in Guangzhou China
Chimelong Xiangjiang Safari Park in Guangzhou, China, is a 130-hectare zoological park with over 20,000 animals from 450 species, including endangered international animals. It features two sections: "Safari on Foot" and "Safari on Wheels," with over 460 species and more than 100 white tigers. The park is highly recommended for families with kids.
Balboa Park: A Cultural Oasis and Botanical Gem in San Diego California
Balboa Park in San Diego is a 1,200-acre cultural park with attractions such as museums, theaters, gardens, shops, and restaurants. The park features Spanish Colonial Revival architecture, including the latticed Botanical Building and the Bea Evenson Fountain. With its beautiful scenery, free parking, and diverse exhibits, it's a must-visit destination worth spending a day strolling around, even if you don't visit any specific attractions.
Exploring Old Town San Diego State Historic Park in California
The Old Town San Diego State Historic Park commemorates the early days of San Diego's town and features historic buildings from 1821-1872. The park preserves adobes, shops, restaurants, and museums showcasing life in Old Town during the Mexican and American periods. It was once the commercial hub but lost popularity to New Town after Alonzo Horton promoted development there in the 1860s.
Wild Wonders of the World Famous San Diego Zoo in California
The San Diego Zoo is a progressive zoo with over 4,000 animals of more than 800 species. The zoo offers guided tours, a Skyfari gondola lift for aerial views, and shows like the Sea Lion Show and An Avian Adventure featuring birds from around the world. The Elephant Odyssey exhibit features a 2.5-acre elephant habitat with three African and four Asian elephants, as well as other exhibits showcasing ancient Southern California species.
First Taste of Ice Cream for Our Twins At One Year 2 Months Old
The blog features a photo shoot of twin babies at 1 year and 2 months old, during the summer season. They try ice cream for the first time, capturing priceless moments of their reactions. The post is an informal update with a playful tone, sharing a lighthearted moment from the family's life.
One Year of Double the Love: Celebrating Serena and Hubert First Birthday
The blog post is a heartfelt message from the author's twin babies' mother, celebrating their 1st birthday with love and affection. She expresses her deep emotional connection with her children, wishing others could experience the same joy and wonder of parenthood. The post invites readers to join in congratulating Serena and Hubert on their special day.
Victoria Park in Full Bloom: My Visit to the 2009 Hong Kong Flower Show
The Hong Kong Flower Show 2009 attracted over 538,000 visitors to Victoria Park from March 13-22. Around 200 organizations from 20 countries showcased exotic flowers, landscapes, and floral art displays. Competitions included the Exhibit, Student Drawing, and Photo Competitions, with results posted for the Exhibit Competition.
Returning to Beijing for the Year of the Ox: A Family Reunion in Beijing China
The author flew back to Beijing on January 25, 2009, just before the Chinese Lunar New Year. They were excited to celebrate with family during the Spring Festival, which features traditional food like dumplings symbolizing family reunion. The author wishes readers a Happy Chinese New Year and hopes the year of the Ox brings good health, prosperity, success, and happy returns.
Photography is a way of feeling, of touching, of loving. What you have caught on film is captured forever it remembers little things, long after you have forgotten everything. - Aaron Siskind
Celebrating Our Twin First Christmas
The author shares their excitement about celebrating baby's first Christmas as a twin addition to the family. They attended a friend's party and received gifts for the twins, but since they're too young to open them, everyone instead opened the gifts together for a fun and festive experience.
The Compound Joy: Navigating the Wonderful World of Parenting Twins
This blog post is not about technology but a personal reflection of having twins, expressing the joy and love that comes with parenting two children at once. It's a heartwarming and relatable account from a parent who cherishes the unique experience of raising twins. There is no mention of technology or a tech-related topic.
Sai Kung Town: A Coastal Gem in Hong Kong
Sai Kung Town developed from a market place around 100 years ago, becoming a scenic tourist location with a wide selection of cuisine. It's famous for its seafood restaurants, but also offers European and Asian food options, making it an "international food and seafood paradise". The town is now known for its diverse dining options, catering to various tastes and preferences.
Three Months of Wonder: Watching Our Twins Grow and Discover
The twin babies are now 3 months old, displaying impressive developmental milestones. They can lift their heads while on their back, wave arms, kick legs, and respond to verbal stimulation with laughter and smiles. This age is crucial for language development, as research links higher intelligence levels to early exposure to words. The twins are beginning to interact with their environment, drawing conclusions and responding to mirrors, voices, and noises.
Twin Babies Have Arrived! Double the Bundles, Double the Love!
The blog post celebrates the birth of twin babies in May 2008, expressing excitement about receiving "twice the bundles" and "twice the love." It also looks forward to the joys of having a sister and brother, expecting "double the giggles," "double the grins," and "double the joy."
A Bloom of Beauty: Visiting the Hong Kong 2008 Flower Show
The Hong Kong Flower Show is an annual event promoting horticulture and greening in Hong Kong. It attracts hundreds of thousands of visitors who appreciate flower beauty and share cultivation experiences. The 2008 show featured potted plants, floral arrangements, landscape displays, commercial stalls, and exhibitors from local, Mainland, and overseas organizations.
Sydney's Iconic Waterfront: Opera House, Harbour Bridge, Darling Harbour, and Luna Park in Australia
The blog likely features information and descriptions about iconic landmarks in Sydney, Australia, such as the Sydney Opera House, Darling Harbour, Luna Park, and the Sydney Harbour Bridge. These sites are well-known for their historical significance and popular tourist attractions. The blog may also include details about each location's history, notable events, and insider tips for visitors.
Photography records the gamut of feelings written on the human face, the beauty of the earth and skies that man has inherited, and the wealth and confusion man has created. It is a major force in explaining man to man. - Edward Steichen
Beyond the Crowds: Discovering Zaragoza's Charm on the Way to Barcelona Spain
Barcelona, a city with a rich cultural heritage, was heavily influenced by Antonio Gaudi's works, including Park Guell and the unfinished La Sagrada Familia church. The city offers a mix of Roman ruins, Gothic architecture, and modernista design, with famous landmarks like Casa Balto. Visitors can explore the city's historic sites, street performers on La Ramblas, and affordable prices for some attractions, making it an excellent destination to experience Barcelona's unique culture and architecture.
Journeying Towards Madrid: Andalusia's Charms, Quixote's Windmills, and Historic Toledo in Spain
Madrid, Spain's capital city, has preserved historic neighborhoods with modern infrastructure. The city was visited before Madrid by Córdoba, declared a World Heritage Site in 1984 for its well-preserved Roman and Islamic architecture. Consuegra featured windmills made famous by Don Quixote, while Toledo offered the Alcázar fortress, Gothic Cathedral, and Plaza de España, featuring statues of Cervantes and his characters.
Unique Crossings, Ancient Caves, and Famous Apes in Gibraltar United Kingdom
Visitors can easily cross from Spain into Gibraltar by waving their passport at the border crossing in La Lina. Once through customs, they walk across an airport runway that could be blocked for plane landings. The Rock of Gibraltar features a cave with stalactites and stalagmites, which was once used as an emergency hospital during WWII. A large colony of apes lives on the Upper Nature Reserve, believed to have originated in the 18th century under British rule.
An Andalusian Journey: Flamenco, Grand Cathedrals, Moorish Palaces, and Pata Negra in Sevilla Spain
The blog describes a trip to Sevilla, Spain in 2007, featuring a Flamenco show at El Palacio Andaluz and exploring the city's iconic landmarks such as the Cathedral of Sevilla and Plaza de España. The next day, it visited Granada, home to the Alhambra Palace with its stunning gardens and architecture, including the Generalife palace and Sacromonte hill with its cave dwellings and traditional shops selling Iberian hams.
Exploring Portugal's Soul: Lisbon, Sintra, Fátima & Cabo da Roca in Portugal
Lisbon, Portugal's capital, is a historic city with over 800 km of Atlantic Coast. The city features many notable buildings, including the National Palace in Sintra and the Sanctuary Basilica in Fatima, where apparitions took place. The Belém Tower and Jerónimos Monastery are also must-visit attractions, designated as UNESCO World Heritage sites.
Exploring Southern Vietnam: From Saigon's Pulse to Delta Life and Underground History in Vietnam
Ho Chi Minh City offers a mix of French colonial architecture and Chinese influences with numerous temples. A visit to Notre Dame cathedral, Post Office, and Ben Thanh market showcase the city's unique culture. A day trip to My Tho on the Mekong River and Tay Ninh's Cao Dai temple offer insight into Vietnam's history, including the Cu Chi Tunnels used during the Vietnamese-American War.
A Deeper Look at the Cu Chi Tunnels in Vietnam
The Cu Chi Tunnels are an underground city built by the Viet Cong during the Vietnam War, stretching 120 km north-west of Saigon. Built between 1940s-1975, it was used as an army base and played a major role in North Vietnam's resistance to American forces. Life in the tunnels was harsh with scarce air, food, and water, but also served as a strategic advantage for the Viet Cong, allowing them to evade US forces until their eventual preservation as a war memorial park.
Ancient Mayan Wonders at Chichen Itza Yucatan Mexico
Chichen Itza is a 1500-year-old Mayan pyramid in Mexico's Yucatan peninsula. The site features three sections with distinct styles and is home to the largest ball court in ancient Mesoamerica. A Sacred Cenote dedicated to the Chac God is also located on the premises, featuring steep vertical sides and a natural steam bath area.
Playa del Carmen: The Vibrant Heartbeat of the Riviera Maya in Quintana Roo Mexico
Playa del Carmen, Mexico, is a top destination in the Riviera Maya for shopping, dining, and nightlife. Its Fifth Avenue offers local and international cuisine, stylish beach clubs with spa treatments and aquatic sports, and high-end restaurants serving Mayan cuisine. A ferry connects to Cozumel for day trips to explore the island's scuba diving and snorkeling spots.
Cancun and Beyond: From White Sand Beaches to Ancient Rivers and Xcaret Park in Mexico
Cancun is known for its beaches, perfect weather, and hotel zone on a peninsula. A popular attraction in Cancun is Xcaret Park, which offers aquatic activities, cultural attractions, and shows. The park features over 40 exhibits, including a butterfly pavilion, coral reef aquarium, and underground river swim. The highlight of the park is the "Xcaret Mexico Espectacular" night-time show, a musical journey through Mexico's history with clever staging and good use of lighting and music.
Exploring the Unique World of Beyond Huis Ten Bosch in Nagasaki Japan
Huis Ten Bosch is a theme park in Nagasaki, Japan that recreates 17th-century Holland with real-size replicas of Dutch buildings, including Palace Huis Ten Bosch, built with royal permission. The park features canals, windmills, amusement rides, and shops, surrounded by greenery and forests, with a marina and residential area.
To me, photography is an art of observation. It's about finding something interesting in an ordinary place I've found it has little to do with the things you see and everything to do with the way you see them. - Elliott Erwitt
Longqing Gorge the Ride of the Soaring Dragon in Beijing China
The Longqing Gorge Scenic Area is 90km northwest of Beijing, featuring a unique blend of southern and northern scenery. The gorge covers 119 square kilometers, with a large dam creating a man-made lake that provides a waterfall during summer months. Visitors can take the world's longest elevator ride (258m) to the top of the dam for panoramic views.
The Santa Cruz Lighthouse: A Tale of Time, Tides, and Tribute in California
The Santa Cruz Lighthouse in California was built in 1868 and features a wooden structure with a tower modeled after another light on Ediz Hook, Washington. It was initially lit in 1869 and later changed to a red color to distinguish it from residential lights. The lighthouse was moved inland due to erosion, and its original site is now mostly gone. A new brick lighthouse replaced the old one in 1967.
San Jose Museum of Art: A Downtown Hub for West Coast Creativity in California
The San Jose Museum of Art is an art museum in Downtown San Jose, California, founded in 1969. It features a large permanent collection of West Coast artists from the 20th and 21st centuries, with exhibits that often incorporate different mediums and perspectives. The museum occupies a historic building designed by Willoughby J. Edbrooke, added to the National Register of Historic Places in 1973.
A Garden of Enchanting Beauty: Experiencing the 2006 Hong Kong Flower Show
The Hong Kong Flower Show is an annual event organized by the Leisure and Cultural Services Department. It promotes horticulture and raises awareness about greening, allowing citizens and horticulture enthusiasts worldwide to appreciate flower beauty and share cultivation experiences. The event attracts hundreds of thousands of attendees each year.
Experiencing the Wonders of Singapore Zoo and Night Safari in Singapore
The Singapore Zoo is a well-managed zoo with over 3,200 animals, offering a unique and immersive experience. The Fragile Forest exhibit features butterflies and invertebrates, while the "Wonders of the Wild" animal show showcases intelligent sea lions and otters performing tricks for the audience. The zoo also offers a chance to feed and interact with orangutans and other animals, providing an unforgettable Amazon-style experience.
San Francisco Vibrant Lunar New Year: Welcoming the Year of the Dog in California
The San Francisco Chinese New Year celebration, originating from the 1860s Gold Rush era, is a two-week Spring festival now recognized as the largest market event in Northern California. The event features two major fairs and concludes with the Chinese New Year Parade. Celebrated for over 5,000 years in China, it marks the beginning of the new year with festivities that attract a large crowd.
When I photograph, I try to use my instincts as much as possible. It is when pictures are unconsidered and irrational that they come to life; that they evolve from showing to being. - Jacob Aue Sobol
Discovering Rome: Architecture, Art, and the Magic of a Christmas Visit in Italy
The blogger visited Rome in December 2005 and explored various landmarks including the Colosseum, Pantheon, Vatican Museums, Sistine Chapel, Spanish Steps, and Piazza Navona. They also enjoyed shopping and local cuisine, and took advantage of public transportation, such as the metro, to get around the city.
Icons of Venice: Doge's Palace, St. Mark's Basilica, and the Rialto Bridge in Italy
Visitors took the train to Venice in December 2005, staying at Hotel Pincipe near Santa Lucia station. On their first day, they explored quiet streets on Christmas Day, discovering restaurants open despite most shops being closed. They attended an opera performance at Scuola Grande Di S. Giovanni Evangelista and visited St. Mark's Square the next day, seeing iconic landmarks like Il Palazzo Ducale, the Bridge of Sighs, and St. Mark's Basilica.
From Edo Gardens to Shinto Serenity, Ancient Temples, and Futuristic Islands in Tokyo Japan
Koishikawa Korakuen Garden, Meiji Shrine, and Sensoji are three main attractions in Tokyo. The garden features stroll paths and seasonal beauty; Meiji Shrine honors Emperor Meiji's deified spirits and offers various festivals throughout the year. Sensoji is Tokyo's oldest temple with traditional snacks and shops. Odaiba offers shopping, entertainment, and theme parks, including the Statue of Liberty and National Museum of Emerging Science and Innovation.
Tranquility on Lamma Island and the Dazzle of Victoria Harbour in Hong Kong
Lamma Island is a peaceful retreat with natural scenery, offering an alternative to Hong Kong's hectic life. It has limited property and rent prices, attracting expats, young people, artists, and musicians. The island can be accessed by ferry from Hong Kong Island or Kowloon Peninsula, where the Victoria Harbour is a major attraction with stunning views of lights twinkling at night.
Santa Barbara Treasures: From Beautiful Zoo Vistas to Grand Courthouse Views in California
The Santa Barbara Zoo is a 30-acre attraction with over 500 animals and scenic views of the Pacific Ocean. The zoo features various exhibits, including a carousel, giraffe feeding, and play areas. Visitors can also explore the surrounding area, which includes the Mission Santa Barbara, Stearns Wharf, and the Santa Barbara Museum of Natural History with its vast collections of artifacts and specimens.
Municipal Rose Garden in San Jose California
The San Jose Municipal Rose Garden in California features over 3,500 shrubs representing 189 rose varieties and serves as an official Display Garden for the All-America Rose Selections. Once on probation due to budget cuts, it was reinstated with full accreditation in 2008 and restored in 2010.
Shanghai Zoo: A Spacious Green Oasis and Home to Diverse Wildlife in China
The Shanghai Zoo is a popular attraction in China, featuring over 6,000 animals from 620 species. It has a total area of 743,000 square meters and includes indigenous animals like giant pandas and golden monkeys, as well as foreign species from around the world. The zoo also boasts a large number of gorillas and has significant green areas with native trees and plants.
Shanghai Temples, Treasures, and Traditional Gardens in China
Shanghai's Jade Buddha Temple features two 1,900-year-old jade statues of the Sakyamuni Buddha, as well as ancient sculptures, paintings, and Buddhist scriptures. The Shanghai Museum boasts a collection of over 120,000 pieces of Chinese art and artifacts, while Yu Garden is a classical Chinese garden with over 30 pavilions linked by corridors and bridges over ponds, including the iconic Huxining Teahouse and Bridge of Nine Turns.
Zhouzhuang China No. 1 Water Town Water in Jiangsu China
Zhouzhuang Water Town is a famous water township in Jiangsu, China, known for its cultural background, preserved ancient houses, and traditional architecture. Built on half a square kilometer of land, 60% of structures date back to the Ming and Qing Dynasties. It's a popular destination with unique snacks like Wansan pig shank and various local dishes, recognized as a UNESCO World Cultural Heritage Site and Grade AAAAA Tourist Destination.
Wildlife Encounters and Serene Gardens at San Franciso Zoo in California
The San Francisco Zoo, located in southwestern SF, has over 693 animals from 197 species across five zoogeographic regions. A visit also included the Japanese Tea Garden in Golden Gate Park, featuring traditional Japanese landscaping with a Buddha statue, waterfall, and tea house, offering a serene oasis amidst the park's beauty.
Heritage Rose Garden San Jose California
The Heritage Rose Garden in San Jose, California features over 3,600 antique and modern roses, making it one of the largest public rose gardens in the western hemisphere. Maintained primarily by volunteers, visitors can learn about rose care or simply enjoy the garden's diverse plants, including lilacs, fruit trees, and a variety of flowers, creating a serene and welcoming atmosphere for relaxation and leisurely strolls.
Lights, Camera, Las Vegas: A Photography Trip to Las Vegas Nevada
Las Vegas is a 24/7 city with plenty of activities. The area has numerous luxurious hotels, including Mandalay Bay, Luxor, Bellagio, and others, all within a short distance. The author attended the NAB tradeshow and took their camera to capture some fun photos, which are shared in this blog post.
Hakone Garden: A Serene Japanese Oasis in Saratoga California
Hakone Garden, located in Saratoga, California, is the oldest surviving Japanese-style residential gardens in the Western Hemisphere. It features various elements of Japan's ancient civilization, including hillside gardens, historic buildings, waterfalls, and koi ponds, blending art and nature for a serene experience. The concept of cultivating nature in miniature dates back to 538 AD with the introduction of Buddhism to Japan.
Shanghai Iconic Skyline: Ascending the Oriental Pearl Tower in China
The Shanghai Oriental Pearl Tower is 468m high, making it the highest in Asia and third in the world. It features 15 spheres of varying sizes, resembling "large and small pearls" on a jade plate. The tower includes a revolving teahouse and sightseeing platform offering panoramic views of the Bund and Pudong New area, with two elevators covering 40 seconds to reach the highest sphere.
Breathtaking Views at the Lake Louise in Banff Calgary Canada
Banff, located 126 km west of Calgary, Alberta, Canada, is the highest-elevation town in Canada with a peak elevation of 4,799.9 ft. The Fairmont Chateau Lake Louise hotel offers breathtaking scenery on its eastern shore of Lake Louise, situated within the UNESCO World Heritage Site Rocky Mountain Parks and built up from an original structure at the end of the 19th century.